
Maxillary nerve Branches, course (preview) Human Anatomy Kenhub YouTube
Treatment. The maxilla is a bone which helps to make up the skull. It is specifically located in the mid face, forms the upper jaw, separates the nasal and oral cavities, and contains the maxillary sinuses (located on each side of the nose. One of the maxilla's most important functions is to make up the architecture of our faces and to support.

Maxillary nerve branches 2 YouTube
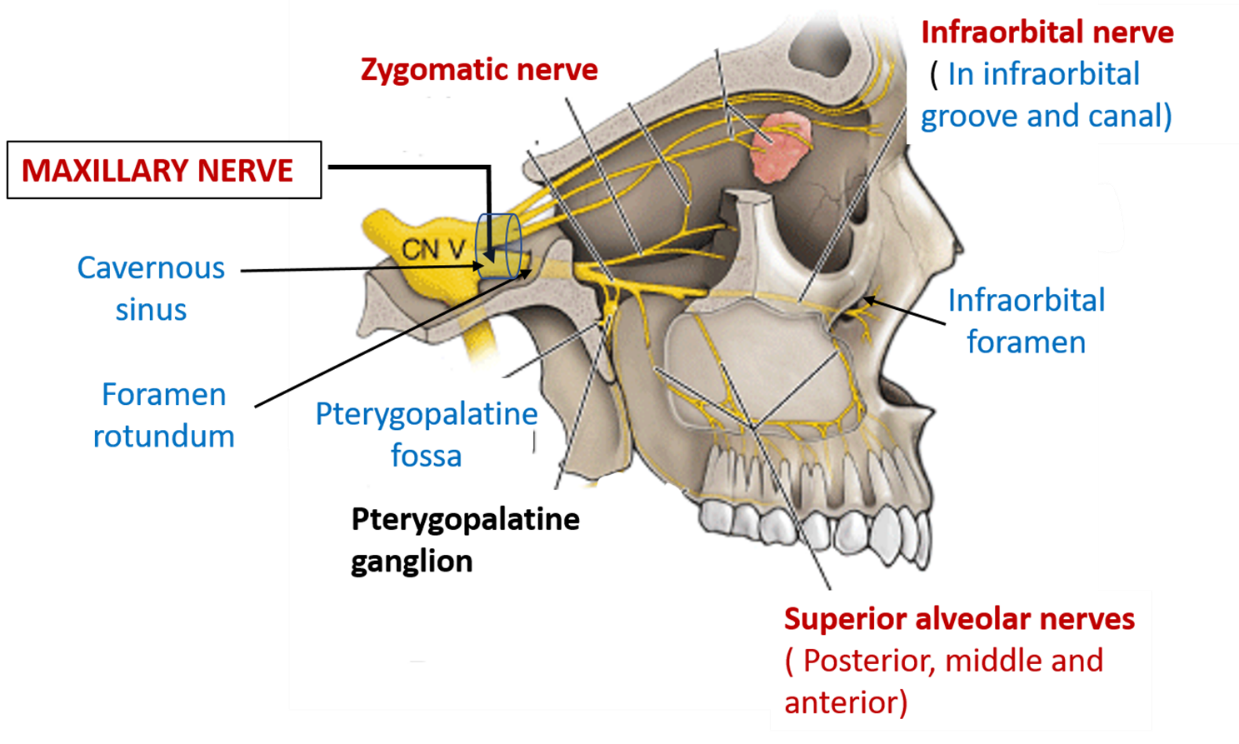
As we've seen, the maxillary nerve runs forwards from the trigeminal ganglion, and enters the foramen rotundum, which is here. Here's the foramen rotundum in the dry bone. We'll go round to the outside to see where it emerges. Here it is, well hidden in the pterygo-maxillary fissure.

Figure 1 from Anatomy and clinical significance of the maxillary nerve a literature review
The maxilla is the most important bone of the midface. It has a central location and provides structural support to the viscerocranium. It has functional and aesthetic significance as it has a fundamental role in facial architecture, separates the nasal and oral cavities, forms the upper jaw, and contains the maxillary sinus. [1] [2] Go to:

Maxillary Nerve Lateral View Diagram Quizlet
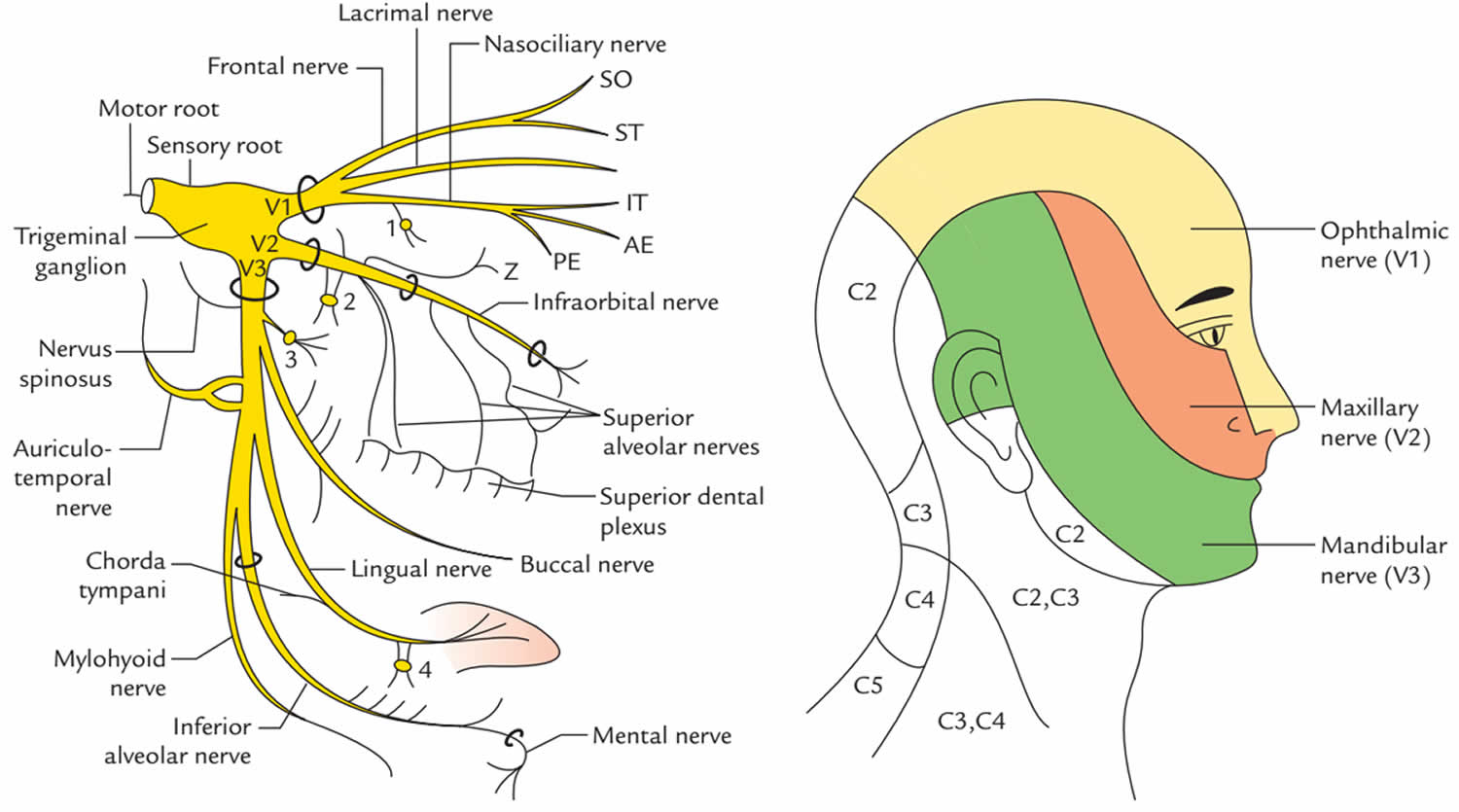
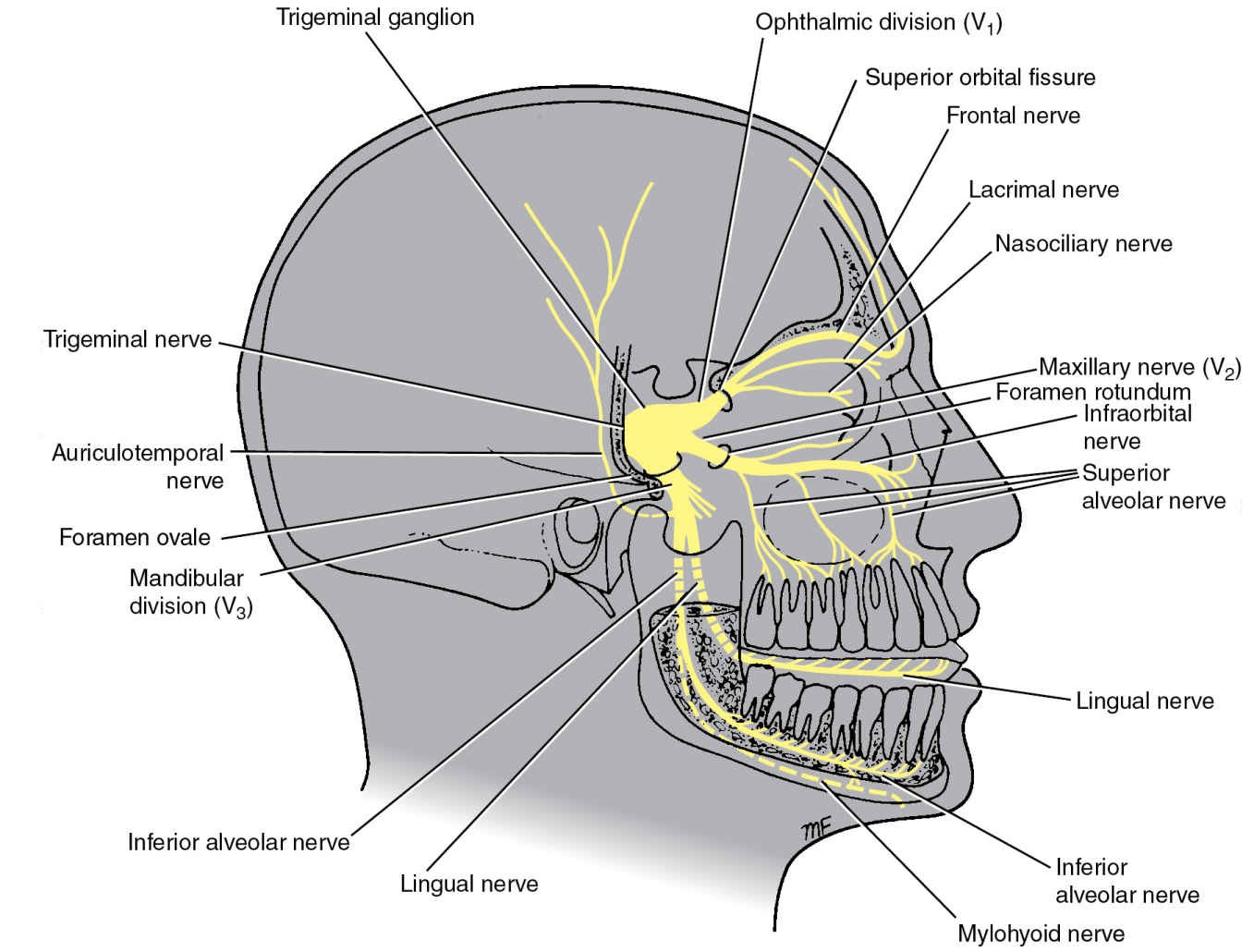
The Maxillary Nerve [Vb; V2] (n. maxillaris; superior maxillary nerve), or second division of the trigeminal, is a sensory nerve. It is intermediate, both in position and size, between the ophthalmic and mandibular. It begins at the middle of the semilunar ganglion as a flattened plexiform band, and, passing horizontally forward, it leaves the skull through the foramen rotundum, where it.
Branches Of Maxillary Nerve slidesharedocs
The maxillary nerve is the second branch of the trigeminal nerve, which originates embryologically from the first pharyngeal arch. Its primary function is sensory supply to the mid-third of the face. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the maxillary nerve - its anatomical course, sensory and parasympathetic functions. Anatomical Course

Maxillary Nerve & Its branches Anatomy mbbs education bds headandneckanatomy nerves YouTube
The maxillary nerve is the second of three branches of the trigeminal nerve. It arises between the trigeminal's ophthalmic and mandibular divisions in a region called the trigeminal ganglion, a cluster of nerves involved in relaying sensory information to the brain as well as chewing motor function.

PPT INFRATEMPORAL FOSSA II MAXILLARY NERVE & VESSELS PowerPoint Presentation ID1377415
In neuroanatomy, the maxillary nerve ( V2) is one of the three branches or divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth (CN V) cranial nerve.

Maxillary Nerve Medical anatomy, Anatomy and physiology, Dental hygienist school
PMID: 31194417 Bookshelf ID: NBK542277 Excerpt The fifth cranial nerve, known as the trigeminal nerve (V), is the largest of the twelve cranial nerves and carries both sensory and motor fibers. It has three terminal branches, which in descending order are ophthalmic nerve (V1), maxillary nerve (V2), and mandibular nerve (V3).
Maxillary Nerve , Origin, Course and Branches , Anatomy QA
The maxillary sinus is intimately related to the roots of the posterior maxillary teeth; the high frequency of mucosal disease and sinusitis of odontogenic aetiology is now well recognized.
Superior Maxillary Nerve ClipArt ETC
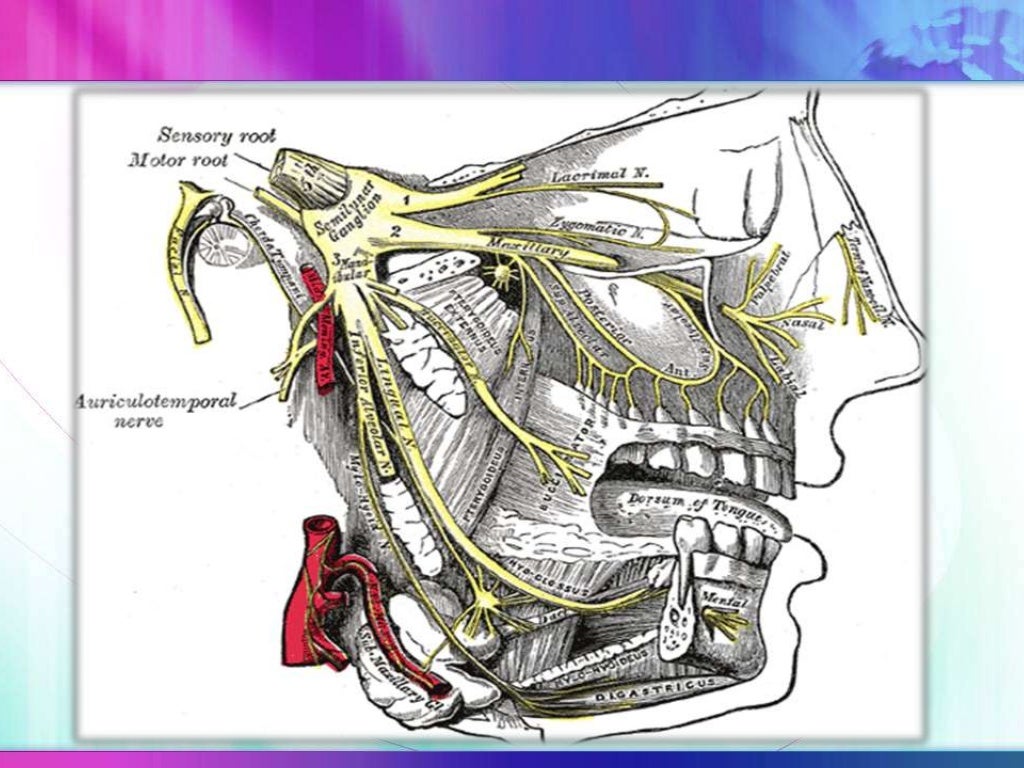
The maxillary nerve arises from the anterior convexity of trigeminal ganglion between ophthalmic and mandibular divisions of the trigeminal nerve. It is a medium-sized branch compared to the smaller ophthalmic nerve and the larger mandibular nerve.

Anatomy and clinical significance of the maxillary nerve a literature review. Semantic Scholar
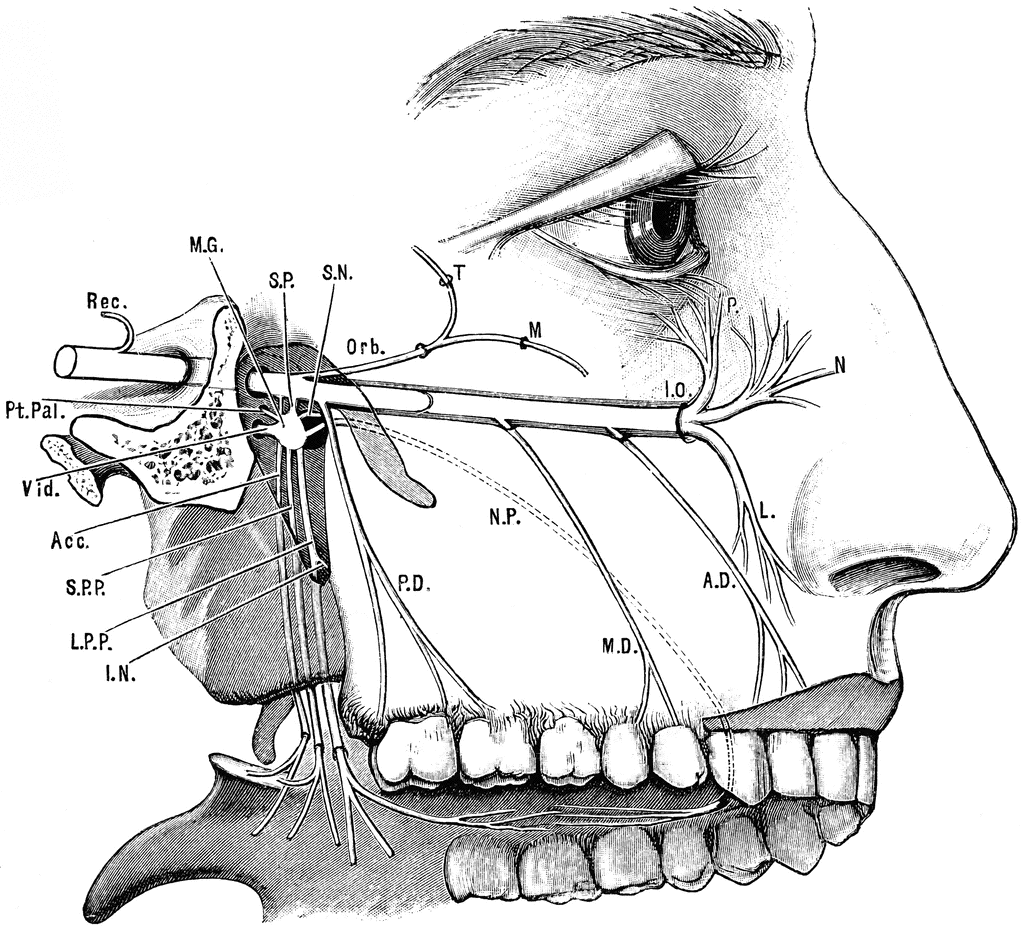
The maxillary nerve emerges from the anterior portion of the trigeminal ganglion, just inferior to the ophthalmic nerve. It runs anteriorly, passing through the lateral portion of the cavernous sinus until it reaches the foramen rotundum. It passes through the foramen rotundum to enter the upper pterygopalatine fossa.
The maxillary nerve
Maxillary nerve is the 2nd branch of the trigeminal nerve. INTRODUC. Let's learn the course and branches of the maxillary nerve in this video in a unique way.

Maxillary Nerve Origin, Course and Branches
Maxillary Nerve. The maxillary nerve, or second division of the trigeminal, is a sensory nerve that crosses the pterygopalatine fossa, traverses the orbit in the infraorbital groove and canal in the floor of the orbit, and appears upon the face at the infraorbital foramen as the infraorbital nerve. From: Cosmetic Facial Surgery, 2011.

Diagram of the second branch (maxillary) of the trigeminal nerve with its branches. Nerve
The maxillary nerve (CN V2, Latin: nervus maxillaris) is the second branch or division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), also known as the maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve.

Maxillary nerve branches 4 YouTube
The maxilla, also known as the upper jaw, is a vital viscerocranium structure of the skull. It is involved in the formation of the orbit, nose and palate, holds the upper teeth and plays an important role for mastication and communication.
The Cranial Nerves Radiology Key
The maxillary nerve (V2) is the middle sized branch of the trigeminal nerve - the largest of the cranial nerves. The V2 is a purely sensory nerve supplying the maxillary teeth and gingiva, the.